Have you ever thought about how technology can shape the way we grow food? Picture a farmer using the Python Application Agriculture with Global Map to monitor crop health from a home computer. The integration of global mapping technology has made such scenarios possible. Let’s dive into the transformative effects of this linked technology on agriculture.
The Rise of Technology in Agriculture
In recent years, technology has made a significant impact on agriculture. With the world’s population growing, farmers are turning to innovative solutions to meet the increasing demand for food. The integration of technology in farming practices is not just a trend; it’s a necessity. So, how is technology reshaping agriculture today?
Increased Crop Productivity Through Tech Tools
One of the most noticeable changes in agriculture is the use of technology to boost crop productivity. Farmers are now using various tech tools that enhance their ability to grow more food with fewer resources. This includes:
- Smart sensors: These devices monitor soil moisture and nutrient levels, allowing farmers to make informed decisions about irrigation and fertilization.
- Drones: Drones are used for aerial imagery, helping farmers assess crop health and identify issues before they become serious problems.
- Mobile apps: There are numerous apps available that help farmers track weather patterns, market prices, and even manage their farm operations.
By utilizing these tools, farmers can significantly increase their yield while also conserving resources. Isn’t it fascinating how a small device can lead to a bountiful harvest?
Automation in Farming Practices
Automation is another area where technology is making waves in agriculture. Traditional farming methods often require a lot of manual labor. However, with the rise of automated systems, many tasks can now be performed with minimal human intervention. Here are a few examples:
- Robotic harvesters: These machines can pick fruits and vegetables faster than human workers, reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency.
- Automated irrigation systems: These systems can adjust the water supply based on real-time data, ensuring crops receive the right amount of moisture without wasting water.
- AI-driven analytics: Farmers can use artificial intelligence to analyze data from various sources, helping them make better decisions about planting and harvesting.
Automation not only saves time and effort but also enhances precision in farming practices. Imagine a farm where machines do the heavy lifting while farmers can focus on strategy and planning!
Rise of Precision Farming Methods
Precision farming is becoming increasingly popular in modern agriculture. This method involves using technology to monitor and manage field variability in crops. It’s all about maximizing efficiency and minimizing waste. Some key components include:
- GPS technology: Farmers can use GPS to map their fields and apply inputs, such as fertilizers and pesticides, more accurately.
- Data analytics: By analyzing data collected from various sources, farmers can identify patterns and optimize their farming practices.
- Variable rate technology: This allows farmers to apply inputs at different rates across a field, depending on the specific needs of each area.
This approach not only increases productivity but also promotes sustainable farming practices. Isn’t it impressive how technology can help us grow food more responsibly?
“Technology is redefining how we grow food and manage farms.” – Food Tech Expert
In conclusion, technology has become a cornerstone of modern agricultural practices. It allows farmers to optimize yields and resources, ensuring that we can feed a growing population. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the ways we approach farming. The future of agriculture is bright, and it’s exciting to think about what’s next!
Understanding Global Mapping in Agriculture

Have you ever wondered how farmers know the best times to plant? Or how they can predict crop yields? The answer often lies in global mapping. This technology plays a crucial role in modern agriculture, helping farmers make informed decisions based on geographic data.
Definition of Global Mapping
So, what exactly is global mapping? Simply put, it’s the process of creating visual representations of geographic data. This data can include anything from soil types to weather patterns. By using tools like Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Global Positioning Systems (GPS), farmers can analyze their land in once-impossible ways.
Think of global mapping as a detailed map of your favorite city. Just as a city map shows streets and landmarks, global mapping provides insights into agricultural fields. It helps farmers understand the lay of the land, making it easier to plan their planting and harvesting schedules.
Applications of Global Mapping in Agriculture
Global mapping has a wide range of applications in agriculture. Here are a few key uses:
- Precision Farming: Farmers can use mapping data to apply fertilizers and pesticides only where needed. This reduces waste and increases efficiency.
- Crop Monitoring: Satellite imagery allows farmers to monitor crop health from above. They can see which areas are thriving and which need attention.
- Soil Analysis: Mapping helps in identifying soil types and conditions. This knowledge aids in selecting the right crops for specific areas.
- Water Management: Global mapping can help in planning irrigation systems. By understanding water sources and drainage patterns, farmers can conserve water.
Each of these applications contributes to more sustainable farming practices. But how does this technology benefit farmers?
Benefits of Using Geographic Data in Farming Practices
Using geographic data in farming comes with a host of benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Farmers can save time and resources by targeting specific areas of their fields.
- Higher Yields: With better data, farmers can make more informed decisions, leading to improved crop yields.
- Cost Savings: By reducing waste and optimizing resource use, farmers can lower their operational costs.
- Environmental Protection: Precision farming techniques help minimize the impact on the environment, making agriculture more sustainable.
As a GIS specialist once said,
“Global mapping offers a 360-degree view of agricultural fields.”
This comprehensive perspective allows farmers to see their land in a whole new light.
Exploring GIS and GPS Technology
At the heart of global mapping are technologies like GIS and GPS. GIS allows for the collection, analysis, and visualization of data. It turns raw data into actionable insights. GPS, on the other hand, provides precise location data. Together, they empower farmers to make decisions based on real-time information.
Imagine being able to pinpoint exactly where to plant each crop type based on soil quality. This is the power of GIS and GPS.
Discussing Satellite Imagery’s Role
Satellite imagery is another vital component of global mapping. It provides a bird’s-eye view of agricultural fields. This imagery can reveal changes in crop health, soil moisture, and even pest infestations. Farmers can use this information to react quickly, preventing potential losses.
In summary, global mapping is transforming the agricultural landscape. By leveraging GIS, GPS, and satellite imagery, farmers can optimize their practices. This not only enhances productivity but also promotes sustainability in farming.
Python’s Role in Agricultural Applications

Python is more than just a programming language; it’s a powerful ally in agriculture. But why is Python so popular in this field? The answer lies in its versatility and ease of use. From data analysis to machine learning, Python can handle it all.
Overview of Python Programming in Agriculture
In agriculture, data is king. Farmers need to make decisions based on data, whether it’s about crop yields, soil health, or weather patterns. Python allows farmers and agricultural scientists to analyze vast amounts of data quickly. This capability leads to better decision-making and improved crop management.
Have you ever wondered how farmers can predict the best time to plant? With Python, they can analyze historical weather data and current conditions to make informed choices. This is just one example of how Python is transforming agricultural practices.
Popular Python Libraries for Data Analytics
When it comes to data analytics, certain Python libraries stand out. Here are a few that are particularly useful in agriculture:
- Pandas: This library is great for data manipulation and analysis. It allows users to work with data frames, making it easier to handle structured data.
- NumPy: NumPy is essential for numerical computing. It provides support for arrays and matrices, which are crucial for performing mathematical operations on agricultural data.
- Matplotlib: Visualization is key in understanding data. Matplotlib helps create graphs and charts, making it easier to visualize trends in crop yields or weather patterns.
These libraries are not just tools; they are the backbone of agricultural data analysis. They help farmers gain insights from their data, leading to smarter farming practices.
Examples of Python Applications in Crop Management
Python’s applications in crop management are diverse. Here are a few notable examples:
- Precision Agriculture: Farmers use Python to analyze data from sensors placed in fields. This data helps them understand soil conditions and optimize irrigation schedules.
- Yield Prediction: By analyzing historical data, farmers can predict future crop yields. This allows them to plan better and allocate resources efficiently.
- Pest and Disease Management: Python can analyze data from various sources to identify potential pest outbreaks or disease risks. Early detection can save crops and reduce losses.
These examples showcase how Python is not just a programming language but a vital component in modern agriculture. As one tech developer aptly stated,
“Python is an invaluable tool for agricultural data analysis.”
Case Studies from Successful Farms
Looking at successful farms can provide valuable insights into the practical applications of Python. For instance, a farm in California used Python to analyze weather patterns and soil moisture levels. This analysis led to optimized irrigation practices, resulting in a 20% increase in crop yield. Another farm in Iowa implemented a data-driven pest management system using Python, which significantly reduced pesticide use and improved crop health.
These case studies highlight the real-world impact of Python in agriculture. They demonstrate how data-driven decisions can lead to more sustainable and profitable farming practices.
In summary, Python’s role in agriculture is growing. Its libraries and applications enable farmers to harness the power of data. Whether it’s improving crop management or optimizing resource use, Python is changing the way agriculture operates.
Data Visualization Techniques for Farmers

Understanding the Importance of Data Visualization in Agriculture
Have you ever wondered how farmers make decisions? The answer often lies in data. In agriculture, data visualization plays a crucial role. It helps farmers interpret complex data sets and transform them into actionable insights. Imagine looking at a field and seeing not just crops, but a wealth of information about soil health, moisture levels, and pest activity. That’s the power of visualization.
Good data visualization is key to making informed agricultural decisions. It allows you to see patterns and trends that would otherwise remain hidden in raw data. For example, a simple graph can show how weather patterns affect crop yields over time. This insight can guide your planting decisions and improve harvest outcomes.
Tools and Libraries to Visualize Agricultural Data
Now that you know why data visualization matters, let’s explore some tools and libraries that can help you visualize agricultural data effectively. Here are a few popular options:
- Tableau: This user-friendly software allows you to create stunning visualizations without needing extensive coding knowledge.
- Power BI: A great tool for integrating various data sources and creating interactive reports.
- Python Libraries: Libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn, and Plotly offer powerful options for those comfortable with coding.
- GIS Software: Geographic Information Systems (GIS) tools help you visualize spatial data, which is essential for precision farming.
Each of these tools has its strengths. For instance, if you’re not tech-savvy, Tableau or Power BI might be the best choice. On the other hand, if you enjoy coding, Python libraries can give you more customization options.
How Visual Data Aids Decision-Making in Farming
Visual data does more than just look good; it aids decision-making in several ways:
- Identifying Trends: Visualizations help you spot trends over time, like how crop yields change with different planting dates.
- Resource Management: By visualizing water usage or fertilizer application, you can optimize resources and reduce waste.
- Risk Assessment: Charts and maps can help you assess risks, such as drought or pest infestations, allowing for proactive measures.
For example, if you notice a consistent drop in yield in a specific section of your farm, you can investigate the cause. Is it due to soil quality, pests, or water availability? With visual data, these questions become easier to answer.
Real-world Applications of Data Visualization
Farmers around the world are already reaping the benefits of data visualization. In the United States, many farmers use satellite imagery to monitor crop health. This method allows them to identify problem areas quickly and address them before they become major issues.
In another case, a vineyard owner used data visualization to analyze weather patterns and soil moisture levels. By correlating these factors with grape quality, they improved their wine production significantly. This kind of insight can make a huge difference in profitability.
As you can see, the applications are endless. Whether you’re a small farmer or managing a large agricultural operation, adopting data visualization techniques can enhance your decision-making process.
In conclusion, embracing data visualization in agriculture is not just a trend; it’s a necessity. By utilizing the right tools and understanding how to interpret visual data, you can make better decisions that lead to increased efficiency and productivity on your farm.
Case Studies: Successful Integrations of Python and Global Mapping
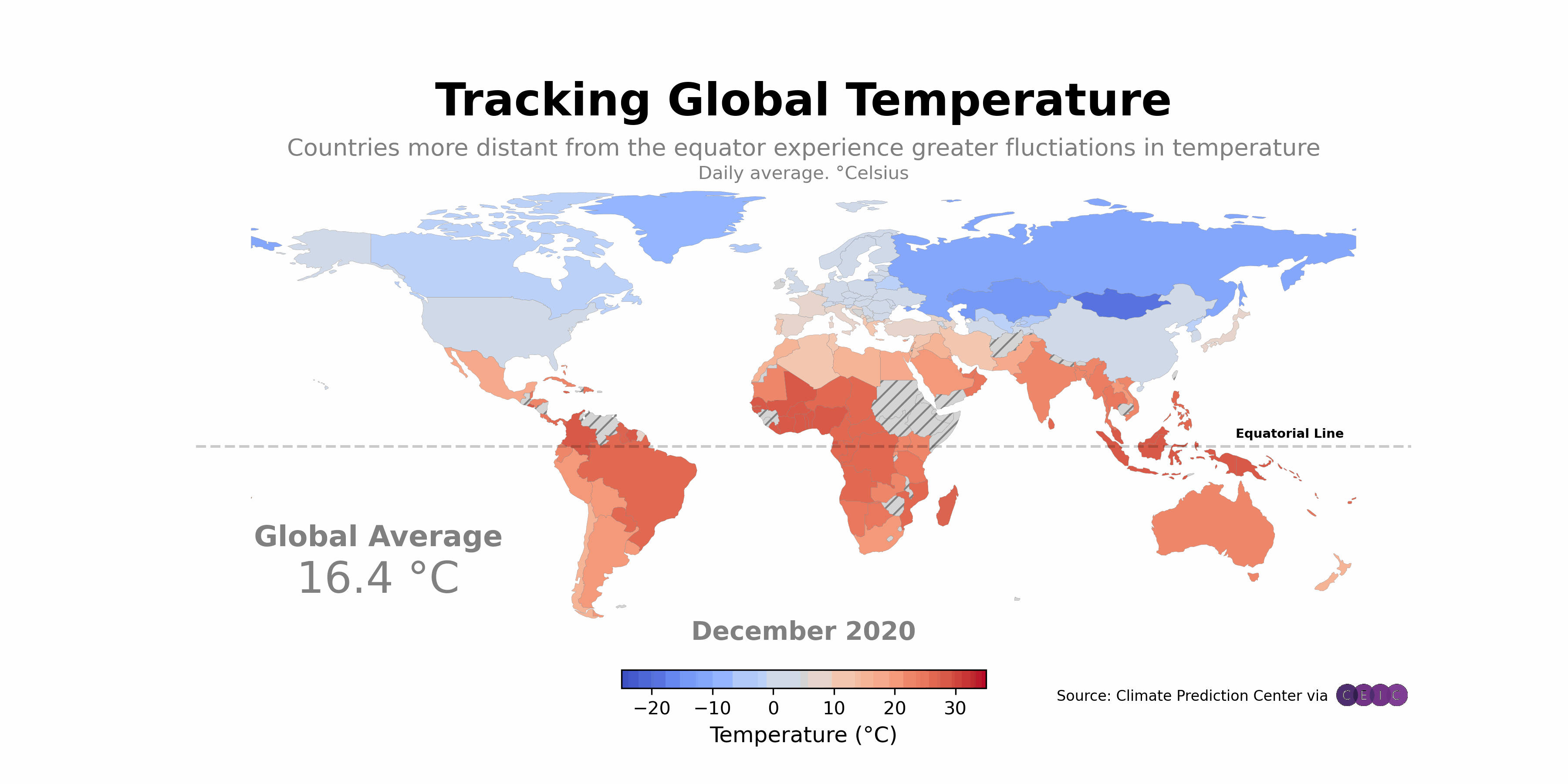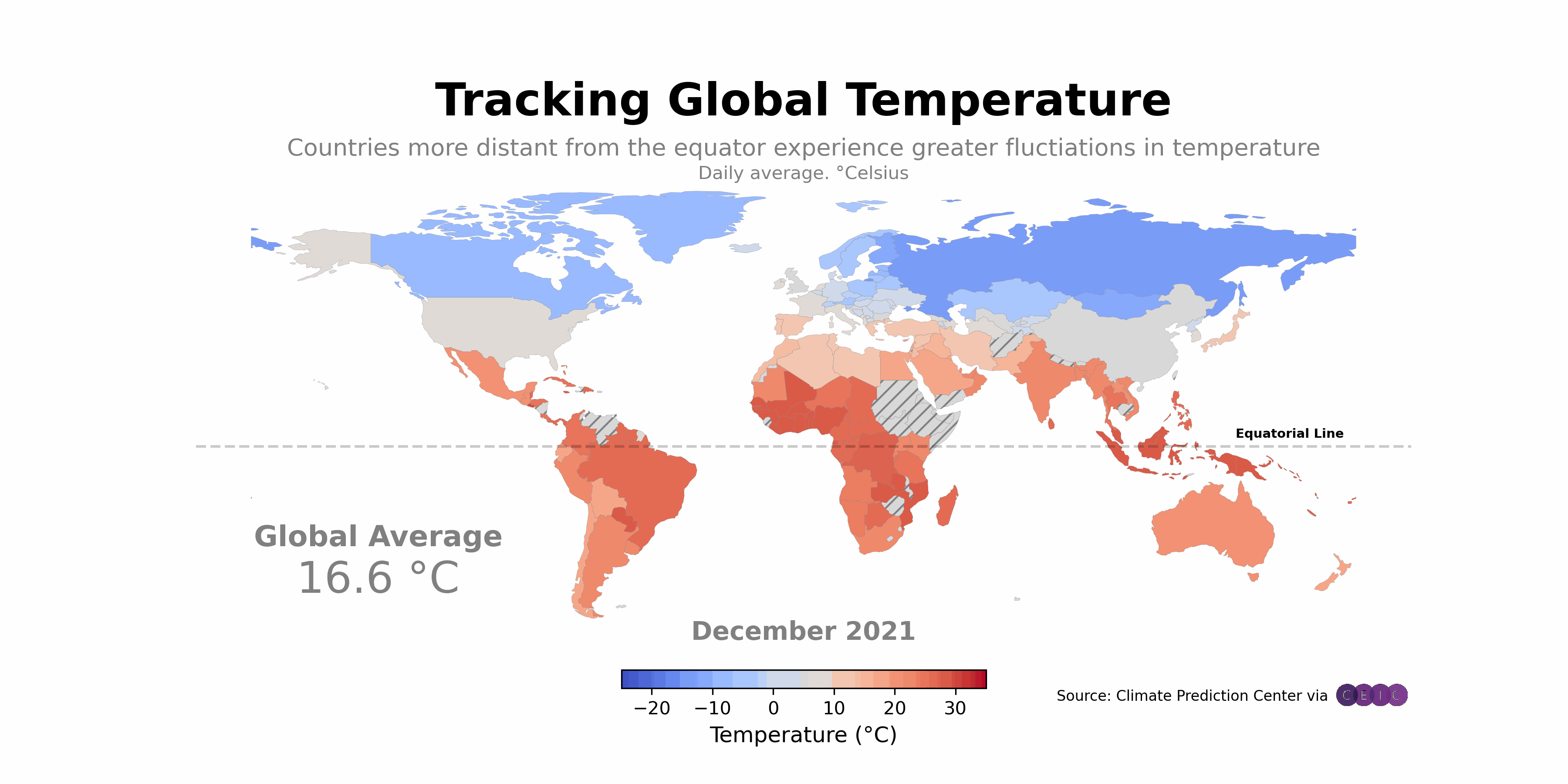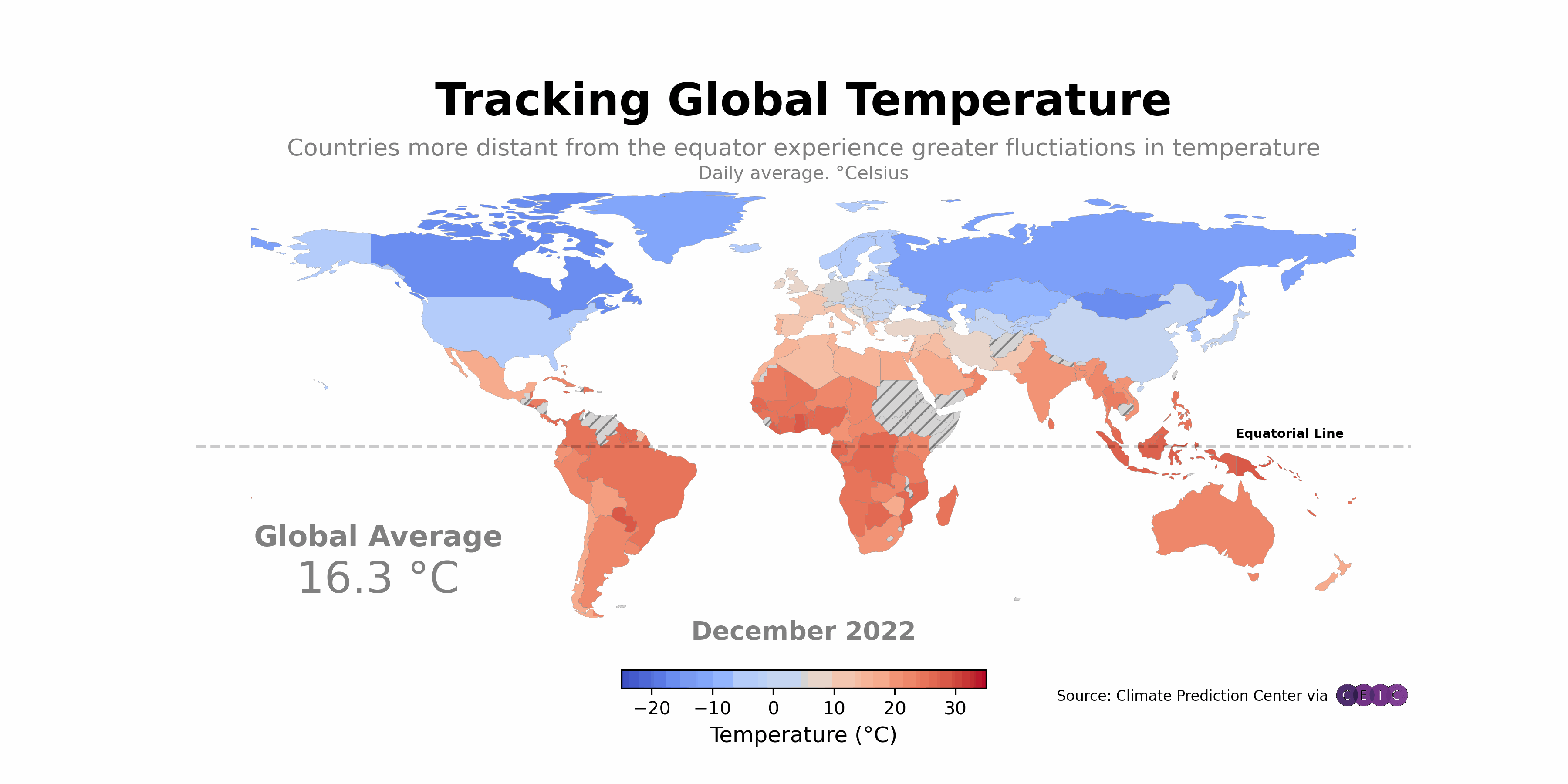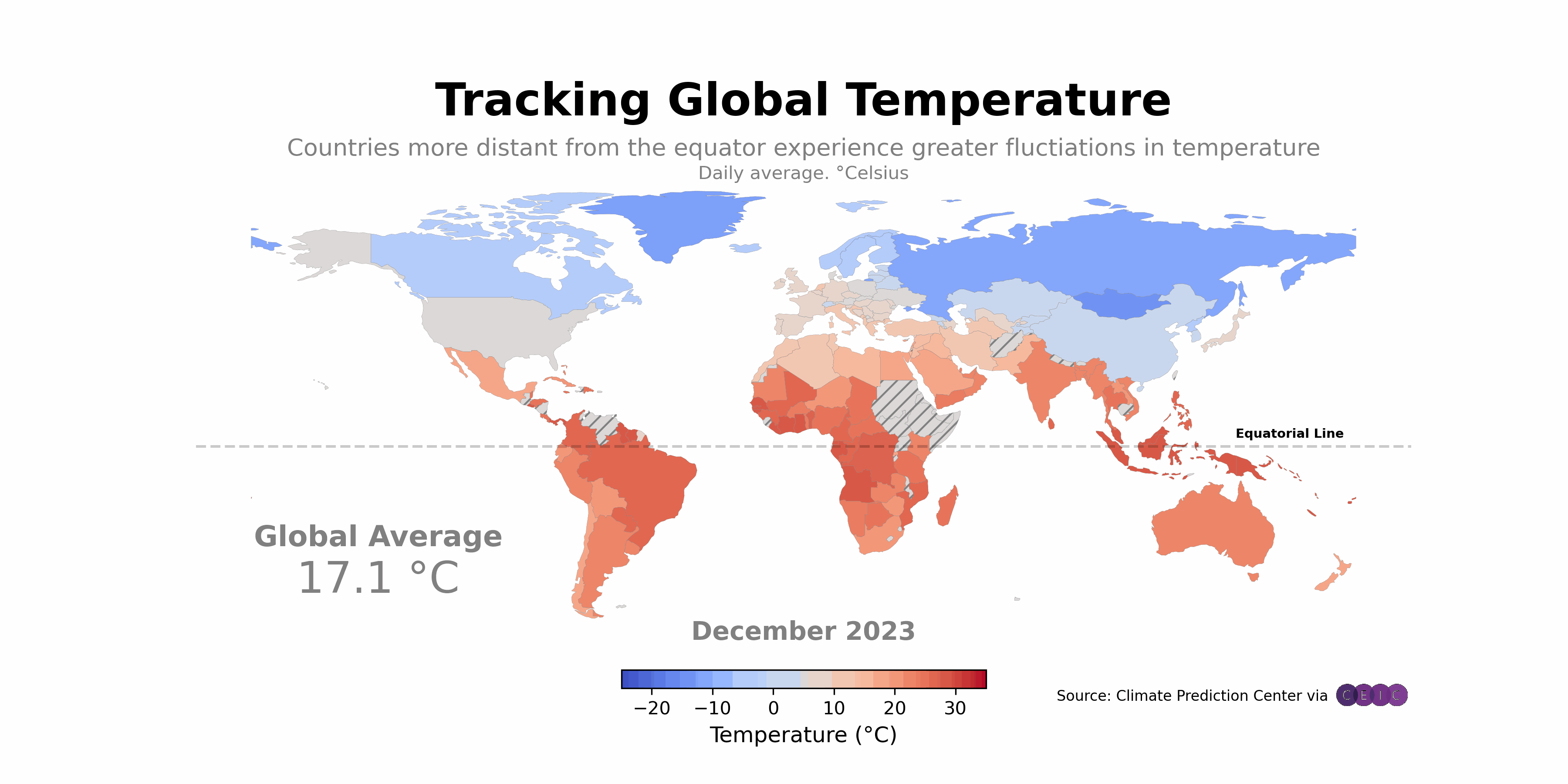
Have you ever wondered how technology can transform agriculture? Imagine farmers using Python and global mapping to enhance their crop yields and manage resources more efficiently. This isn’t just a dream; it’s happening right now. Let’s explore some real-life examples that highlight the impact of these technologies.
1. Highlighting Specific Farmers and Organizations
One standout example is the Farmers’ Cooperative in Iowa. This organization adopted Python applications integrated with global mapping tools to monitor their fields. They utilized satellite imagery and Python scripts to analyze soil health and crop growth. The results were impressive.
- Before Integration: Farmers relied on traditional methods, which often led to guesswork in resource allocation.
- After Integration: With Python and global mapping, they gained precise data on soil conditions, enabling targeted interventions.
Another notable case is the AgTech Startup in California. They developed a Python-based application that helps farmers visualize their fields through global mapping. This tool allows farmers to track water usage, pest infestations, and crop health in real time.
2. Impact on Crop Yields and Resource Management
So, what happens when farmers use these technologies? The results speak for themselves. The Iowa Cooperative reported a 25% increase in crop yields after implementing the new system. By using data-driven insights, farmers could apply fertilizers and water only where needed. This not only boosted production but also reduced waste.
Similarly, the California AgTech startup found that farmers using their application saved 30% more water compared to conventional methods. This is crucial, especially in areas prone to drought. Efficient resource management is not just beneficial; it’s essential for sustainable agriculture.
3. Providing Quantitative Results from These Integrations
Quantitative results often tell the most compelling stories. Here are some key statistics from these case studies:
- Iowa Cooperative: 25% increase in crop yields
- California AgTech: 30% reduction in water usage
- Overall: Farmers reported a 40% decrease in input costs due to better resource allocation.
These numbers demonstrate the tangible benefits of integrating Python and global mapping into agricultural practices. As an agricultural expert noted,
“Seeing tangible results from these technologies can inspire more farmers to adopt similar methods.”
4. Sharing Before and After Scenarios
Let’s take a moment to reflect on the transformation. Before these technologies, farmers often worked with limited information. They relied on intuition and experience, which could lead to inefficiencies.
After the integration, the landscape changed dramatically. Farmers now have access to real-time data that informs their decisions. They can see where to plant, when to irrigate, and how to manage pests effectively. This shift not only increases productivity but also enhances the sustainability of farming practices.
In conclusion, these case studies illustrate the power of technology in agriculture. By integrating Python applications with global mapping, farmers are not just surviving—they’re thriving. The human element of these stories adds depth to the technological advancements, showcasing how innovation can lead to better lives for farmers and a more sustainable future for agriculture.
Challenges of Integrating Technology in Agriculture

Integrating technology into agriculture can be a double-edged sword. On one side, it offers incredible opportunities for efficiency and productivity. On the other, it comes with its own set of challenges. Let’s explore these hurdles so you can be better prepared to navigate them.
Common Pitfalls in Tech Adoption
When it comes to adopting new technology, many farmers face common pitfalls. Here are a few to keep in mind:
- Lack of Knowledge: Many farmers may not fully understand how a new technology works. This lack of knowledge can lead to improper use or even avoidance of the technology altogether.
- Overconfidence: Some may believe they can manage without tech, thinking their traditional methods are sufficient. This mindset can hinder progress.
- Ignoring Training: Technology often requires training. Skipping this step can lead to mistakes and wasted resources.
So, how can you avoid these pitfalls? Start by educating yourself and your team. Attend workshops, webinars, or even local meet-ups focused on agricultural technology. Knowledge is power!
Resistance Among Traditional Farmers
Resistance to change is natural, especially in traditional farming communities. Many farmers have relied on the same methods for years, and introducing technology can feel daunting. Why change what has worked for so long?
However, it’s essential to understand that technology can complement traditional methods rather than replace them. Here are some ways to ease this transition:
- Showcase Success Stories: Highlight farmers who have successfully integrated technology. Real-life examples can inspire others to consider the benefits.
- Involve the Community: Engage local farmers in discussions about technology. Their input can help tailor solutions that fit their needs.
- Provide Support: Offer ongoing support and resources for those hesitant to adopt new tech. A helping hand can make a big difference.
Cost of Implementing Technology
Cost is often a significant barrier to tech adoption in agriculture. New equipment, software, and training can add up quickly. You might wonder, is it worth the investment?
While the initial cost can be high, consider the long-term savings and efficiency gains. Here are some tips to manage costs:
- Start Small: Consider implementing technology in phases. This approach allows you to spread out costs and learn as you go.
- Look for Grants: Many organizations offer grants for farmers looking to adopt new technology. Research available options in your area.
- Calculate ROI: Assess the potential return on investment. Understanding how technology can improve yields or reduce labor costs can justify the expense.
“Every innovation faces hurdles; understanding them is crucial for success.” – Innovator
While technology offers great prospects, challenges must be addressed to ensure successful integration in farms. By being aware of these hurdles, you can take proactive steps to overcome them.
Remember, change is never easy. But with the right mindset and resources, you can successfully integrate technology into your farming practices. Embrace the possibilities that come with modern agriculture!
The Future of Agriculture with Python and Global Mapping

The agricultural landscape is changing. With advancements in technology, farmers now have tools that can help them make better decisions. One such tool is Python, a programming language that is becoming increasingly popular in agriculture. But how does this all work? What does it mean for you as a farmer or someone interested in agriculture? Let’s explore.
1. Predicting Trends in Agricultural Technology
As we look to the future, it’s essential to understand the trends shaping agricultural technology. Here are some key points:
- Data-Driven Decisions: Farmers are using data analytics to predict crop yields and manage resources more efficiently.
- Precision Agriculture: This involves using GPS and IoT devices to monitor crop health and soil conditions.
- Automation: Robotics and drones are on the rise, helping with planting, monitoring, and harvesting.
These trends show a clear shift towards integrating technology into farming. But why is this important? Simply put, it helps you maximize your output while minimizing waste.
2. Potential Innovations in the Coming Years
Innovation is at the heart of agricultural technology. Here are some potential breakthroughs you might see:
- Enhanced Crop Varieties: Genetic engineering is leading to crops that can withstand harsh conditions.
- Smart Irrigation Systems: These systems use sensors to optimize water usage, saving both money and resources.
- Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency: This technology can track the journey of food from farm to table, ensuring quality and safety.
Imagine a world where you can check the history of your product with a simple scan. This isn’t just a dream; it’s becoming a reality.
3. The Role of Education and Training in Adoption
But how do we get there? Education and training are crucial. Here’s why:
- Tech-Savvy Youth: Young people are more open to adopting new technologies. They can drive change in traditional farming practices.
- Workshops and Online Courses: These resources can help farmers learn about new tools and techniques.
- Community Involvement: Local organizations can play a significant role in providing training and support.
Are you ready to embrace these changes? The future of farming lies at the intersection of technology and tradition. As a farmer, you have the opportunity to be part of this exciting evolution.
4. A Call to Action for Farmers
Now, let’s talk about action. As a farmer, you might be wondering where to start. Here are a few steps you can take:
- Research: Look into the latest technologies and see what fits your needs.
- Connect: Join local agricultural groups or online forums to share knowledge and experiences.
- Experiment: Don’t be afraid to try new tools on a small scale before fully committing.
By taking these steps, you can position yourself at the forefront of agricultural innovation. Remember, the potential for future advancements in agricultural technology can reshape practices globally.
In conclusion, the future of agriculture is bright. With tools like Python and global mapping, the possibilities are endless. Are you ready to be part of this transformation?
FAQs About Python Application Agriculture with Global Map
When it comes to integrating Python and global mapping in agriculture, many questions come to mind. Farmers and tech professionals alike often seek clarity on how these technologies can benefit them. Below, we address some of the most common queries.
1. What are the best Python libraries for agriculture?
Python offers a variety of libraries that can significantly enhance agricultural practices. Here are some of the top choices:
- Pandas: This library is essential for data manipulation and analysis. It allows you to work with structured data easily.
- NumPy: Great for numerical calculations, NumPy is often used in agriculture for modeling and simulations.
- Matplotlib: This is a plotting library that helps visualize data. You can create graphs to represent crop yields or weather patterns.
- Scikit-learn: If you’re interested in machine learning, Scikit-learn is a must. It’s used for predictive analysis, helping farmers make informed decisions.
- GeoPandas: This library extends Pandas to allow spatial operations on geometric types, which is particularly useful for mapping agricultural data.
Using these libraries, you can analyze data, predict outcomes, and visualize trends effectively. They are not just tools; they are gateways to smarter farming practices.
2. How does global mapping improve yield?
Global mapping can be a game changer for farmers. But how exactly does it work? Think of it like having a bird’s-eye view of your fields. Here are a few ways global mapping can help:
- Precision Agriculture: By using mapping technologies, you can apply resources like water and fertilizers more efficiently. This targeted approach reduces waste and maximizes yield.
- Soil Analysis: Mapping can reveal variations in soil quality across your land. Understanding these differences allows for better crop selection and management.
- Weather Patterns: With global mapping, you can track weather trends and predict conditions that affect your crops. Being prepared helps mitigate risks.
- Pest and Disease Management: Mapping technologies can help identify areas at risk for pests or diseases, enabling timely interventions.
In essence, global mapping equips you with the information needed to make proactive decisions, ultimately leading to improved crop yields.
3. Is it expensive to start using these technologies?
The cost of integrating Python and global mapping into your agricultural practices can vary widely. Here are some factors to consider:
- Initial Investment: You may need to invest in software, hardware, and training. However, many Python libraries are open-source and free to use.
- Long-term Savings: While the upfront costs might seem high, the potential for increased efficiency and yield can lead to significant savings over time.
- Scalability: Start small. You can gradually scale your use of technology as you see the benefits. This approach minimizes risk and spreads out costs.
In conclusion, while there may be some initial expenses, the long-term benefits of using Python and global mapping in agriculture can outweigh these costs. You’ll not only enhance your farming practices but also contribute to a more sustainable future. By embracing these technologies, you position yourself at the forefront of modern agriculture.

